 The six neighborhoods of Tehran are located on a line starting from the historical core towards the west and northwest of the city. The selected neighborhoods reflect different urban form patterns and socioeconomic characteristics. The residents of Type 1 neighborhoods are mostly from lower-income families, while those living in Type 2 and 3 neighborhoods are considered to be among medium-income households. Selection of higher-income regions located in the north of the city, such as the municipal Region 1 of the city, has been avoided to have a good representativeness regarding socioeconomic factors.
The six neighborhoods of Tehran are located on a line starting from the historical core towards the west and northwest of the city. The selected neighborhoods reflect different urban form patterns and socioeconomic characteristics. The residents of Type 1 neighborhoods are mostly from lower-income families, while those living in Type 2 and 3 neighborhoods are considered to be among medium-income households. Selection of higher-income regions located in the north of the city, such as the municipal Region 1 of the city, has been avoided to have a good representativeness regarding socioeconomic factors.
Sangalaj (Typ I)
 This area is among the Tehran’s oldest neighborhoods and has been the scene of several historical political events in the nineteenth century. During and after the WW II, the neighborhood could not continue its successful presence in the history of Tehran and lost its importance as a hub of social affairs and political movements.
This area is among the Tehran’s oldest neighborhoods and has been the scene of several historical political events in the nineteenth century. During and after the WW II, the neighborhood could not continue its successful presence in the history of Tehran and lost its importance as a hub of social affairs and political movements.
On the northern side, the City Park (Park-e Shahr) is located, which was built after the world war to combat deterioration. Today, more than one-third of the area of this neighborhood is considered to be deteriorated texture. With 107ha area and 29359 inhabitants, the area has a compact and organic urban form with many culs-de-sac and curvy and broken narrow streets.
Arg-Pamenar (Typ I)
This neighborhood is attached to Sangalaj from northeastern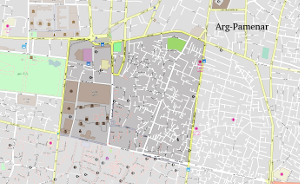 side and to the Grand Bazaar and neighborhood of Bazaar from the northern side. The urban land use is quite like Sangalaj. This area has had a unique social, cultural, and political importance in the nineteenth-century Tehran, during the reign of Qajar Dynasty. Today the neighborhood has a population of 5869 and area of 120ha. A high percentage of the population consists of the youth.
side and to the Grand Bazaar and neighborhood of Bazaar from the northern side. The urban land use is quite like Sangalaj. This area has had a unique social, cultural, and political importance in the nineteenth-century Tehran, during the reign of Qajar Dynasty. Today the neighborhood has a population of 5869 and area of 120ha. A high percentage of the population consists of the youth.
Towhid (Typ II)
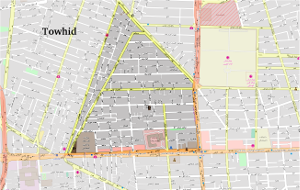 Towhid was first formed in 1960s as a response to the rural-urban migration. Large parts of what is called Towhid neighborhood today were then gardens. The street network is a semi-orthogonal grid with many dead-end allies. Today, the neighborhood has an area of 104ha and a population of 36.106 people
Towhid was first formed in 1960s as a response to the rural-urban migration. Large parts of what is called Towhid neighborhood today were then gardens. The street network is a semi-orthogonal grid with many dead-end allies. Today, the neighborhood has an area of 104ha and a population of 36.106 people
Sadeghieh (Typ II)
This neighborhood was formed in 1950s and 1960s after the 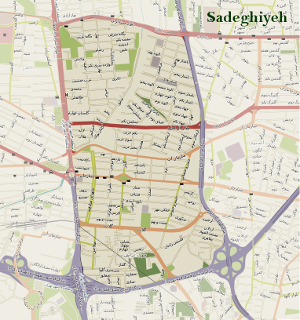 fast population increase of Tehran caused by rural-urban migration and fast urbanization rates. The neighborhood has mostly orthogonal street network with 40.872 inhabitants located in 210ha. Sadeghieh Square located in the west of the neighborhood acts as a city-level node connecting many destinations in western Tehran.
fast population increase of Tehran caused by rural-urban migration and fast urbanization rates. The neighborhood has mostly orthogonal street network with 40.872 inhabitants located in 210ha. Sadeghieh Square located in the west of the neighborhood acts as a city-level node connecting many destinations in western Tehran.
Shahran-Jonoubi (Typ III)
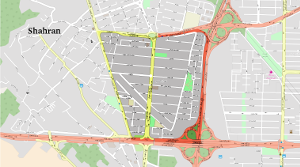 The emergence of the area as a residential neighborhood dates back to about the year 1980. Before that, the area was a good place for spending time outdoors during holidays near to the heights of Northern Tehran enjoying good weather. Like many new quarters, this area has complete gridiron near to motorways easing private car use. This neighborhood covers 89ha surrounded by three urban highways and a main street.
The emergence of the area as a residential neighborhood dates back to about the year 1980. Before that, the area was a good place for spending time outdoors during holidays near to the heights of Northern Tehran enjoying good weather. Like many new quarters, this area has complete gridiron near to motorways easing private car use. This neighborhood covers 89ha surrounded by three urban highways and a main street.
Golestan-Sharghi (Typ III)
This area has been recently developed during the past two decades based on a 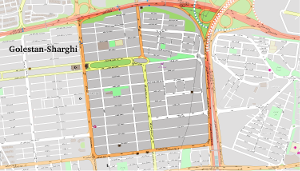 complete orthogonal street network covering 170ha. New residential buildings are four or five-story buildings neat to two large urban highways. The majority of residents living in their personal apartments are from middle class looking for affordable housing units as an investment for future rise in the price.
complete orthogonal street network covering 170ha. New residential buildings are four or five-story buildings neat to two large urban highways. The majority of residents living in their personal apartments are from middle class looking for affordable housing units as an investment for future rise in the price.
